The Importance of Exercise

Dr Michael Burdon
Consultant in Sport, Exercise & Musculoskeletal Medicine
- 11 September, 2019
- Exercise
- 3 min read
The positive effects of physical activity on physical and mental health as well as quality of life have been well documented and is more well known than ever.

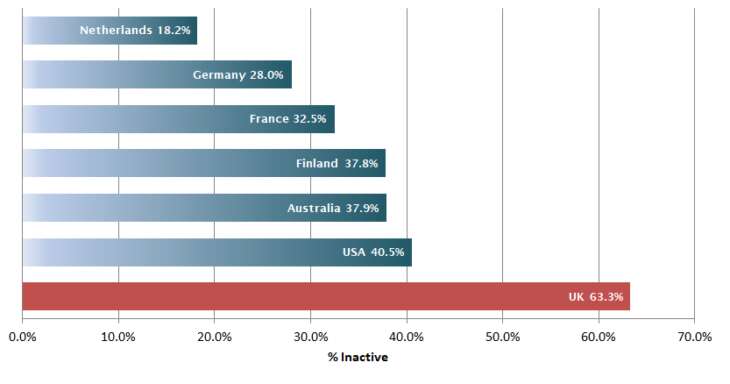
But unfortunately, insufficient activity is a major public health problem. A study done by Public Health showed that the UK had the worst ‘inactivity rates’ compared to the USA, Australia, Finland, France, Germany and Netherlands.
Surprised?
What Are The Benefits of Exercise?
Exercise has significant health benefits and some you may not even realise.
These include reducing risk of cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, lower back pain, depression, anxiety and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), which is an umbrella term used to describe progressive lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and non-reversible asthma. This disease is characterised by increasing breathlessness).
When experiencing chronic conditions such as these, Exercise Physiologists can advise and guide you through training programmes so you’re able to maintain an effective level of exercise.
The table below shows how much physical activity can help reduce the risk of long-term conditions and mortality. For example, doing physical activity can reduce your risk of getting breast cancer by 20%!
| Disease | Risk reduction |
| Death | 20-35% |
| CHD and Stroke | 20-35% |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 35-40% |
| Colon Cancer | 30-50% |
| Breast Cancer | 20% |
| Hip Fracture | 36-68% |
| Depression | 20-30% |
| Hypertension | 33% |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | 20-30% |
| Functional limitation, elderly | 30% |
| Prevention of falls | 30% |
| Osteoarthritis disability | 22-80% |
Start Active, Stay Active (2011) based on US Department of Health and Human Services Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Report (2008)

On top of these long-term conditions, physical activity can help with:
Sleep
Exercise helps you drift off more quickly and into a deeper sleep, allowing a better night’s rest. A good night’s sleep is essential for overall health.
Boost energy levels
The surge of blood around the body transports oxygen to the brain to make you feel mentally alert. It also increases blood flow to the tissue as well as your lungs and heart. Better conditioned muscles and cardiovascular system require less effort to perform physical tasks and over time as the body becomes stronger so too does the immune system reducing the risk of illness.
Memory
Regular exercise has also been shown to improve memory and learning functions, both of which are impaired by chronic stress. Scientists have also discovered that exercise helps in preventing dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Depression
Exercise helps chronic depression by increasing serotonin, which helps your brain regulate mood, sleep and appetite. Immune system chemicals that can worsen depression are also reduced.
Mood
Exercising also releases a chemical called endorphins in the brain, which help to improve your mood.
Reduces inflammation and visceral (abdominal) fat
Increasing physical activity increases muscle activity, which then increases a substance called anti-inflammatory myokines. This in turn reduces systemic inflammation and also reduces the fat around your organs knows as visceral fat. Visceral fat itself can be dangerous and causes an increased risk of dementia, heart disease, diabetes, stroke, breast and colon cancer.

So How Much Exercise Should We Be Doing?
The UK Chief Medical Officers recommend:
- 150 minutes of moderate intensity activity per week OR 75 minutes of vigorous intensity activity per week OR A combination of both.
- Muscle-strengthening activity at least 2 day per week.
- Limit time spent sitting for extended periods (recommend getting up for 2 mins every 20 mins).
- For older adults (65+) – Balance and co-ordination activities at least 2 days per week.

This doesn’t mean that you have to go to the gym every day and lift heavy weights, the most important factor is to pick something that you enjoy doing, make it achievable and build it into part of your daily routine.
For example, getting off one tube stop earlier and walking, take the stairs instead of the lift or escalator, run or cycle into work as part of your normal daily commute, head out for a walk in your lunch break, try a new hobby with some friends – the list is endless and you can get creative with it!
Remember, more is better, and some is better than none.
In 2020 we created a series of 15 minute work outs for all abilities and ages. Why not give these a go today?
References:
- Public health England (2014) Everybody Active, Every Day (2014) based of WHO Observatory date
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/r…
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/r…

Advice
Over the last 20+ years our experts have helped more than 100,000 patients, but we don’t stop there. We also like to share our knowledge and insight to help people lead healthier lives, and here you will find our extensive library of advice on a variety of topics to help you do the same.
OUR ADVICE HUBS See all Advice Hubs

