What Is Osteopathy? Benefits & Treatment Explained

Gareth Degg
Osteopath
- 13 April, 2024
- Osteopathy
- 3 min read
What Is Osteopathy? Benefits & Treatment Explained
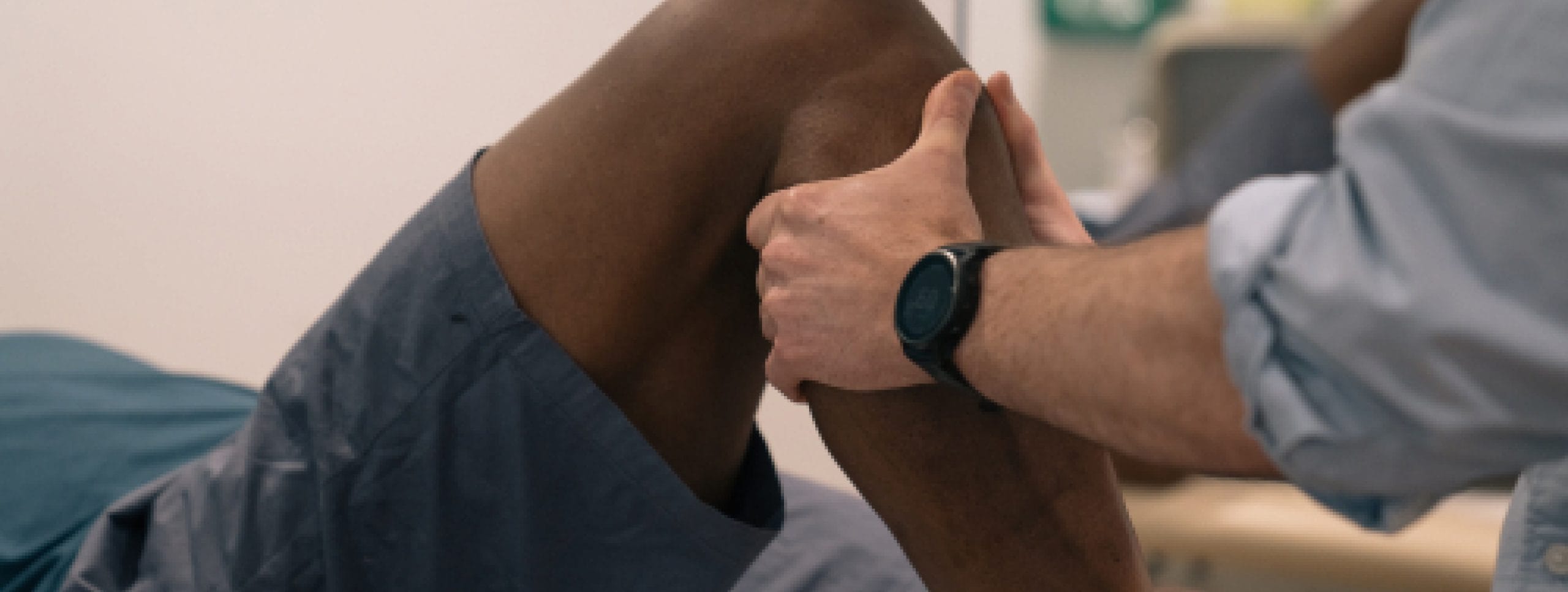

Osteopathy in the United Kingdom holds a significant place in the realm of complementary and alternative medicine.
It is regulated by the General Osteopathic Council (GOsC), ensuring that practitioners meet the necessary standards of education, training, and professional conduct.
Your Osteopath will have undergone rigorous education and training, often completing a four or five-year degree program in osteopathy, which includes clinical experience.
Rooted in the principles established by its founder, Dr. Andrew Taylor Still, osteopathy has evolved into a well-established healthcare profession with a distinct identity within the UK’s healthcare system.
What are the Osteopathic Principles?
Structure and Function are Interrelated: This principle emphasises the interconnectedness of the body’s structure (bones, muscles, ligaments, organs) and its function (movement, circulation, nervous system activity). Osteopaths believe that optimal health depends on maintaining proper alignment and mobility of these structures.
The Body Has Self-Healing Mechanisms: Osteopathy recognises the body’s innate ability to heal itself. Osteopathic treatment aims to support and facilitate the body’s natural healing processes by removing obstacles to health and promoting optimal function.
The Rule of the Artery: This principle highlights the importance of blood flow and circulation in maintaining health. Osteopaths believe that proper blood flow is essential for delivering oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to tissues, as well as for removing waste products and toxins. They focus on improving circulation to support overall health and healing.
The Body is a Unit: Osteopathy views the body as an integrated unit, where all systems are interconnected and influence each other. Dysfunction in one area of the body can affect other areas, so osteopathic treatment aims to address the body rather than focusing solely on symptoms or isolated body parts.
When should I see an Osteopath?
Individuals seeking osteopathic care can choose from a diverse pool of practitioners, ranging from osteopathic physicians who hold medical degrees to osteopathic practitioners or manual osteopaths with specific training in Osteopathy. Regardless of their designation, all osteopaths in the UK adhere to the same professional standards set by the GOsC.
Like the rest of our multidisciplinary team, our osteopaths adopt a holistic approach, viewing the body as an interconnected system where musculoskeletal health plays a pivotal role in overall well-being.
Osteopathy can help with a number of issues, including:
- Sports injuries
- Arthritic pain
- Back pain
- Neck pain, headaches & migraines
- Concussion
- Disc injuries
- Sciatica
- Frozen shoulder or elbow pain
- Joint pain & lumbago
- Muscle spasms
- And more…
What does treatment typically look like?
In practice, you can expect your osteopath to use hands-on manual techniques to assess and treat various conditions, as well as joint mobilisation and soft tissue manipulation. These methods aim to restore mobility, alleviate pain, and enhance the body’s natural healing processes.
Treatment can include:
- Rehabilitation services
- Manual therapy
- Mobilisation & manipulation of joints
- Biomechanical assessments
- Taping
- Dry needling & acupuncture
- Exercise prescription
- And more…
An initial appointment with one of our Osteopaths will include a full musculoskeletal assessment, individualised treatment and a discussion of the treatment plan required to help you achieve your specific goals.
You will leave the appointment with a unique individualised management plan, which will explain the treatment you require including other members of the multidisciplinary team who may be involved in your care.
The Role of Osteopathy in UK Healthcare
The UK’s National Health Service (NHS) recognises osteopathy as a valuable therapeutic option. Osteopaths often work in private clinics, but an increasing number are also integrated into multidisciplinary healthcare teams within NHS settings, providing a complementary approach to conventional medical care.
Research on the efficacy of osteopathy in the UK is ongoing, with some studies supporting its effectiveness for various conditions. While the evidence base continues to grow, many patients in the UK report positive outcomes and improvements in their health through osteopathic treatment.
The scope of osteopathic practice in the UK extends beyond musculoskeletal conditions as osteopaths recognise the interconnectedness of different bodily systems and consider the impact of structural imbalances on overall health.
This comprehensive approach allows osteopathy to address a wide range of health issues, from acute injuries to chronic conditions.
The emphasis on the mind-body connection is a notable feature of osteopathic care. We acknowledge that emotional and psychological factors can influence physical health and consider these aspects when assessing and treating patients.
This aligns with the broader trend in the UK healthcare system, recognising the importance of holistic approaches to patient care.
In summary, osteopathy in the United Kingdom is a well-regulated and respected healthcare profession that embraces the holistic principles of self-healing and balance.
Practitioners employ hands-on manual techniques to address a broad spectrum of health issues, working alongside conventional medical care.
The integration of osteopathy into the UK healthcare system reflects its recognised value in promoting overall well-being and supporting patients on their journey to health and vitality.
References

Advice
Over the last 20+ years our experts have helped more than 100,000 patients, but we don’t stop there. We also like to share our knowledge and insight to help people lead healthier lives, and here you will find our extensive library of advice on a variety of topics to help you do the same.
OUR ADVICE HUBS See all Advice Hubs