What is a Foot Specialist (Podiatrist)?

Pure Sports Medicine
- 16 January, 2019
- Podiatry
- 5 min read
Whether we are running for the bus, jogging on the treadmill or simply walking to work – our feet take a lot of impact in our day to day life. However, unless we injure them it’s unlikely you spend too much time thinking about their health.
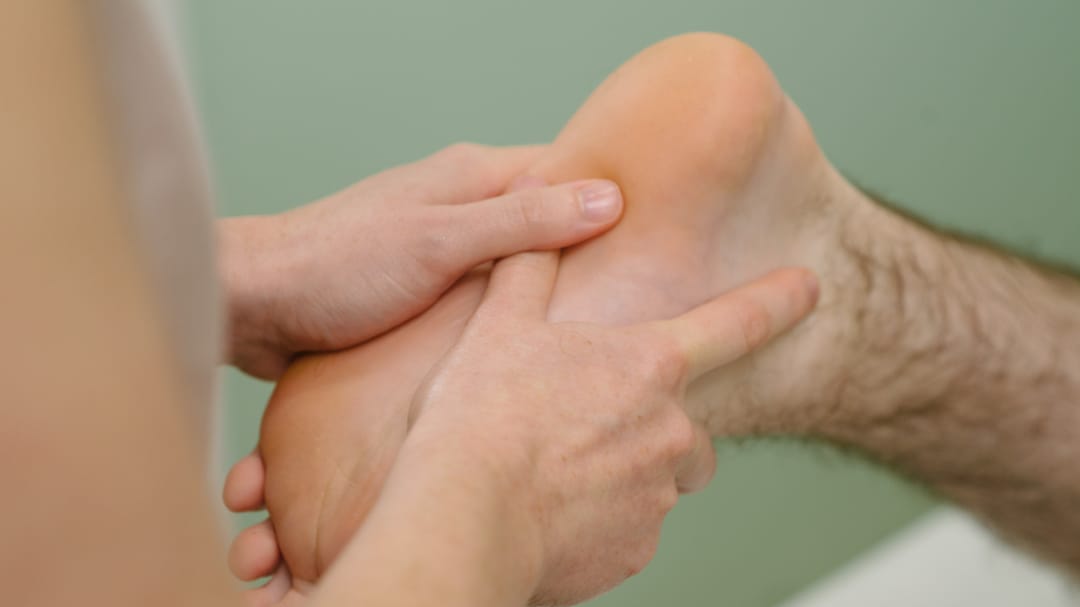
If you have hurt your feet or lower limbs, you may be referred to a Podiatrist. These experts are vital in maximising your recovery and diagnosis, which is why Podiatrists are so important to our multidisciplinary team.
To help you understand where Podiatry fits into the world of Sports Medicine and our multidisciplinary team, we’re going to answer the following FAQs:
- What is Podiatry?
- What does a Sports Podiatrist do?
- How can a Sports Podiatrist help you?
- What happens at the consultation?
- What treatment can a Sports Podiatrist give?
What is Podiatry?
Podiatry is the medical speciality that focuses on the care of the foot and ankle.
Podiatrists are concerned with the examination, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of foot ailments by biomechanical, minor surgical and other treatment methods.
We are often called upon by other Physicians and Health Care Professionals for consultations and treatment of foot problems. Problems which can be experienced by everyone, from children to seniors. After all, you only have one pair of feet to last a lifetime!
What Does a Podiatrist or ‘Foot Doctor’ Do?
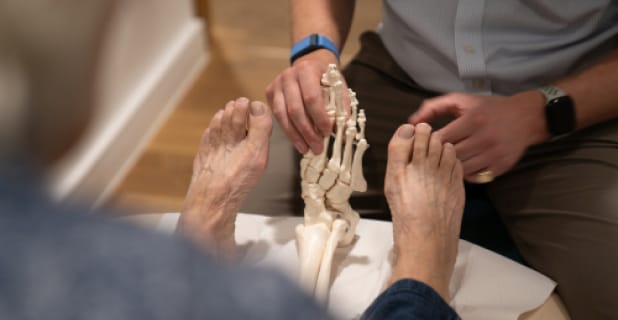
Sports Podiatrists are experts in foot and ankle anatomy and function. Specifically at Pure Sports Medicine, our Team of Podiatrists specialise in musculoskeletal (MSK) podiatry, meaning we look at the relationship of muscles and bones together.
Our work involves looking at how individual variances, such as load and movement pathways, can influence injury and recovery.
The term ‘biomechanics’ refers to the way muscles, bones, and joints work together as we move. When applied to the lower limb, we focus on the biomechanics of impact absorption and propulsion.
It’s important to understand the gait cycle; this includes walking, running or sports specific movements. For example, when running, just after the heel strikes the ground, the foot begins to pronate (roll in). This movement allows the foot and leg to adapt to the terrain and absorb the impact of the foot strike. A certain amount of pronation is necessary to run normally, but too much or too little can contribute to injuries.
When the foot tends to pronate excessively (or at the incorrect time of the gait cycle), the foot becomes structurally unstable and, in turn, the muscles, tendons and ligaments of the lower leg are forced to work harder in an attempt to stabilise the foot.
Common Injuries of Excessive Pronation
- Shin splints
- Plantar calcaneal bursitis (inflammation of the fluid sac which cushions the heel)
- Morton’s neuroma (a condition that affects the nerves between the toes)
- Achilles tendonitis (overuse of the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone)
- Ankle sprains
- Knee injury
Those who have too little pronation (i.e. increased or excessive supination) occurring through the foot when needed can also be a contributing factor. As a certain amount of rigidity is necessary to generate the force needed to run, however, too much supination can decrease the foot’s ability to absorb impact and, therefore, can lead to impact-related sports injuries.
Runners with excessive supination may experience ankle pain and, in severe cases, tend to have a history of recurrent ankle sprains and/or stress fractures. Individuals who experience these injuries require the highest level of cushioning in their shoes and should avoid shoes with stability features.
Common Injuries of Under Pronation
- Calf strain
- Plantar calcaneal bursitis (inflammation of the spongy fluid filled sac that cushions the fascia of the heel and the heel bone)
- Bone shin splints
- Hamstring strain
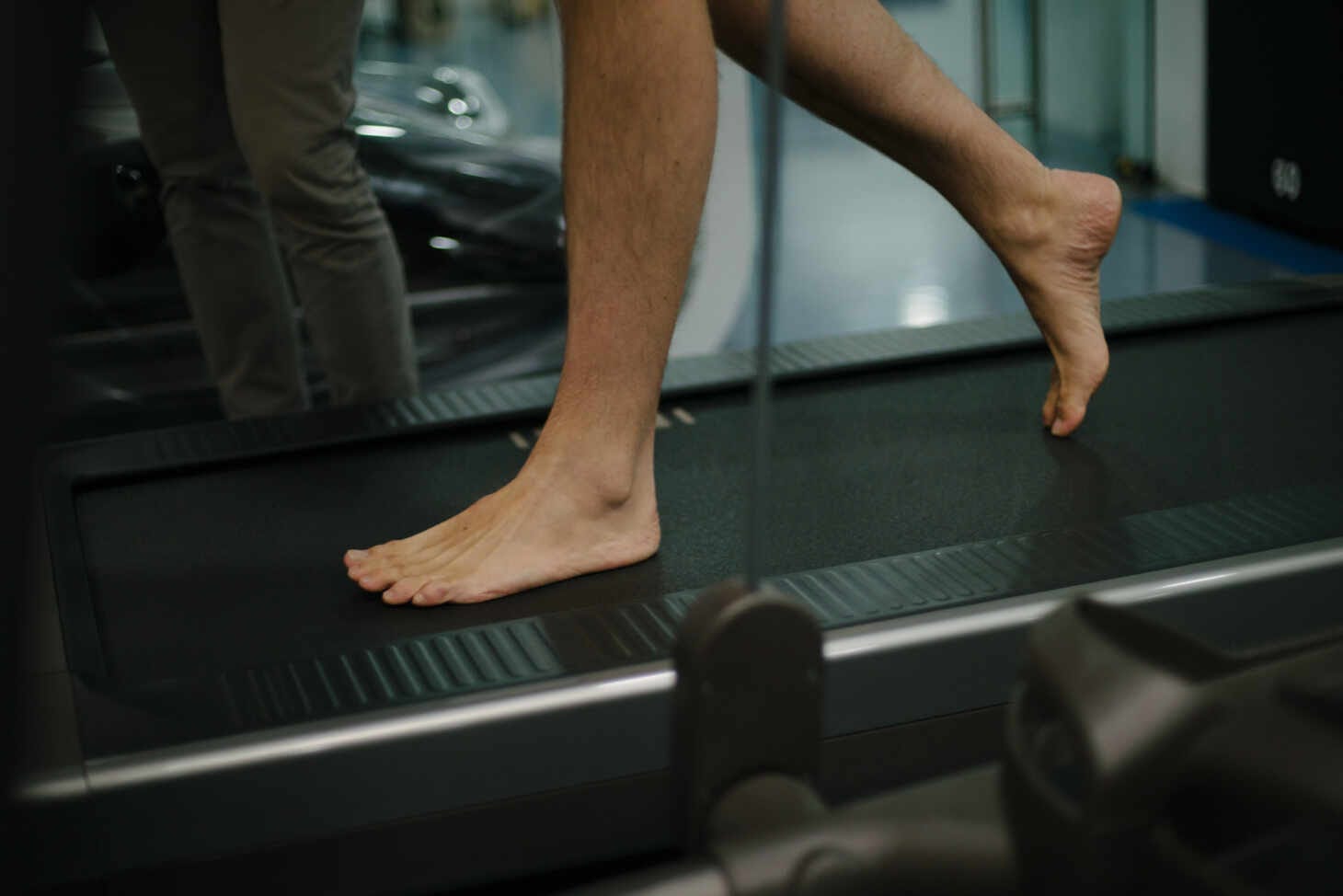

How Can a Podiatrist Help You?
A Sports Podiatrist will analyse the way an individual’s foot strikes the ground and evaluate the chain of motion of the major joints in the leg from the ground up in order to determine whether or not there are any biomechanical reasons that may be contributing to an injury.
By looking at the way the foot moves, the force or ‘load’ being put through it and if relevant, any current or prior injuries, a Podiatrist can assess and suggest treatments to help you reach your goals.
These goals can be related to an injury, such as rehabilitating a sprain, or performance-focused focused like beating your personal best running time.
Typically, our Sports Podiatrists see sub-acute or chronic, longer-term lower extremity pain that has occurred without a particular incident. Such as regular aches in a runner’s ankles or persistent heel pain with walking.
It’s these gradual onsets, which overuse injuries that haven’t resolved as expected, that a Sports Podiatrist’s knowledge base is best equipped to deal with.
What Happens at The Consultation?
Your consultation will begin with finding out necessary details about your injury; this consists of a thorough subjective history of your presenting complaint, including current activity levels, in addition to your future goals.
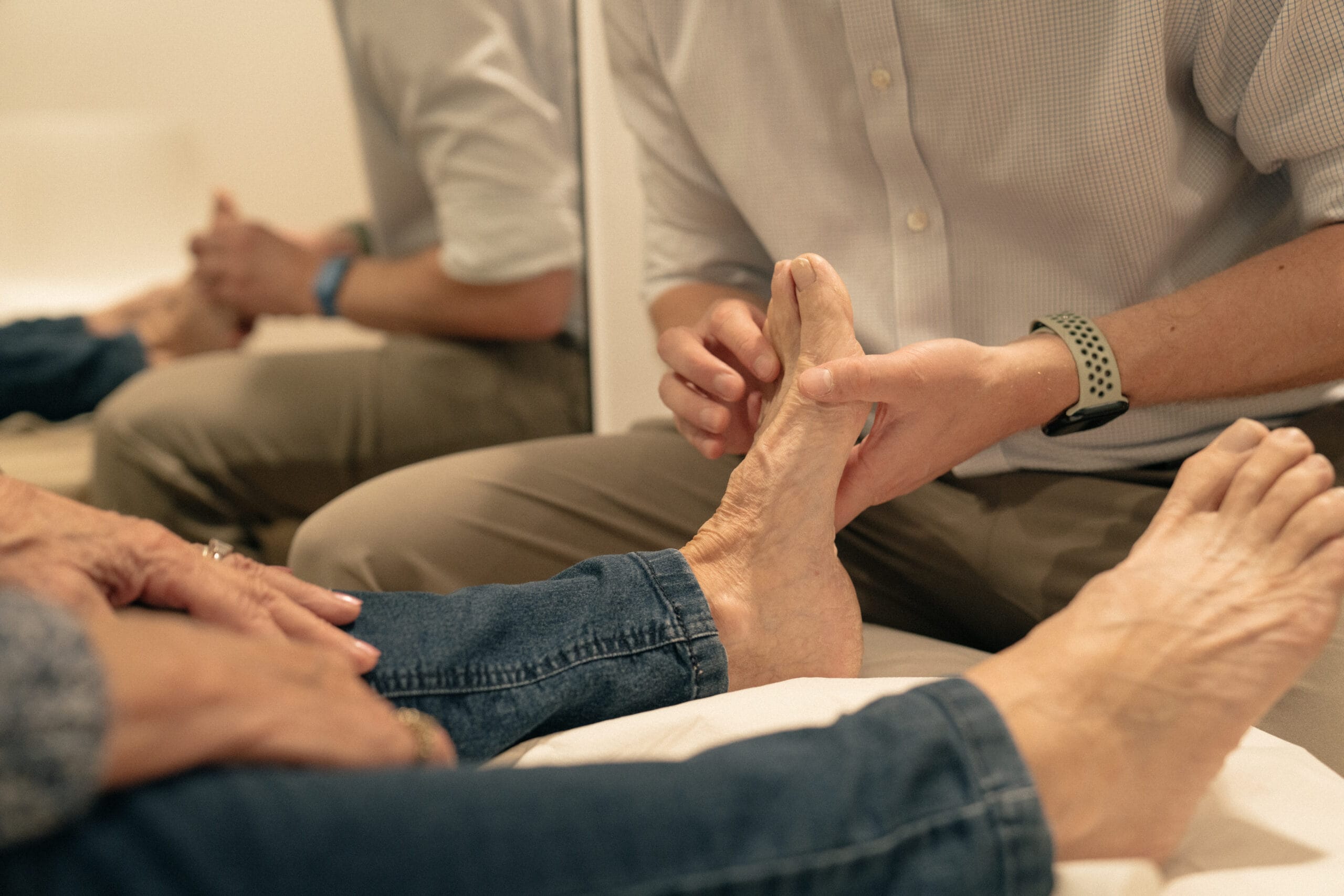
Following this, it is likely that an ‘Initial Gait Analysis’ will be conducted. A Gait Analysis includes a hands-on non-weight-bearing assessment going through your individual lower limb and foot alignment, joint ranges of motion, strengths and special tests depending on your current ailment.
This study is a way of looking at the way you walk or run and is often captured by video and utilised as a diagnostic and/or treatment tool, which helps the Patient to gain further understanding of their individual movement.
Podiatrists can use these assessments to correlate the movement pathways of a particular walking or running gait, in line with the injured structure, as this will provide insight into the amount of load the region is withstanding.
By identifying the issue within the assessment, your Podiatrist can help to manipulate the force being passed through the injured area to a level that is more tolerable. This helps enable healing and further progression with rehabilitation to allow this injured structure to tolerate more load with no added stress or symptoms.
Podiatrists have a strong understanding that there is no perfect movement pathway and that variation between foot and ankle movements is high and normal. We embrace the variation and develop patient-specific clinical models of foot function.
What Treatment Can a Podiatrist Give?
Podiatrist’s conservative treatment options to help assist with your recovery can range from, but are not limited to:
- Footwear advice (running and casual)
- Functional foot orthoses (custom and pre-fabricated)
- Running gait re-training
- Exercise programmes
- Taping & strapping
- Joint mobilisations
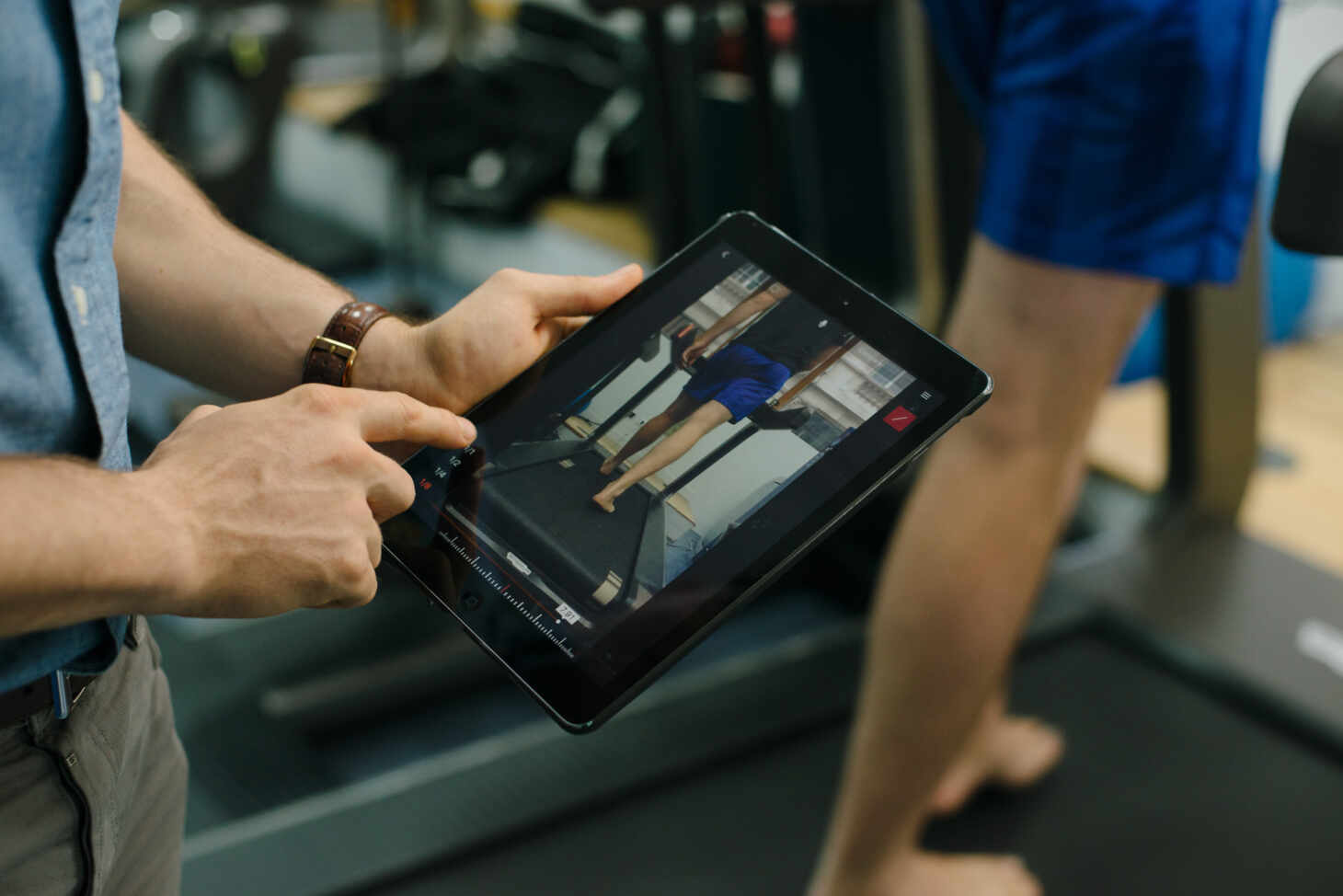

Across our 8 London based clinics, we work closely with our colleagues as part of a multi-disciplinary team. Together with Physiotherapists, Strength and Conditioning Coaches, Osteopaths and other specialists where necessary, we’ll focus on the right recovery path for you. In cases where further investigation or more invasive treatment plans are required, our Podiatrists are closely aligned with our highly regarded Consultants in Sport, Exercise and Musculoskeletal Medicine (SEM) and Foot and Ankle Surgery Consultants across the London area to maximise your care.
If you’re suffering from any foot or ankle pain that is encroaching on your daily or sporting activities, contact our team today and book an appointment to get started on the road to recovery.

Advice
Over the last 20+ years our experts have helped more than 100,000 patients, but we don’t stop there. We also like to share our knowledge and insight to help people lead healthier lives, and here you will find our extensive library of advice on a variety of topics to help you do the same.
OUR ADVICE HUBS See all Advice Hubs